This white paper explores the critical intersection of network management, security, and firewall solutions, drawing upon the systems approach to network design and management.
Network Management, Security, and Firewalls: A Systems Approach
This white paper explores the critical intersection of network management, security, and firewall solutions, drawing upon the systems approach to network design and management.
1. A Systems Approach to Network Management
- Holistic View: The systems approach emphasizes understanding the network as an interconnected system of components. This holistic view is crucial for effective network management and security.
- Key Components:
- Hardware: Servers, routers, switches, firewalls, and other network devices.
- Software: Operating systems, network protocols (TCP/IP, UDP), and applications.
- Users: Individuals and organizations accessing and utilizing the network.
- Data: The information flowing through the network.
- Security: Measures and mechanisms to protect the network and its resources.
- Interdependencies: Recognizing the interdependencies between these components is crucial for effective network management. Changes in one component can have cascading effects on others.
2. Network Security Fundamentals
- Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data.
- Availability: Ensuring that network resources are accessible to authorized users when needed.
- Non-repudiation: Ensuring that the origin and integrity of data can be verified.
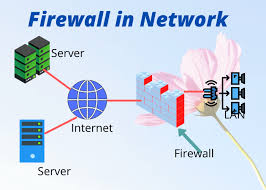
3. The Role of Firewalls in Network Security
- Firewall Functions:
- Packet Filtering: Examining incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocking or allowing packets based on predefined rules.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Translating internal IP addresses to external IP addresses to hide internal network topology.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP/IPS): Detecting and preventing malicious activity, such as malware attacks and denial-of-service attacks.
- Types of Firewalls:
- Packet Filtering Firewalls: Basic firewalls that inspect packet headers and block or allow traffic based on source/destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: Track the state of network connections, allowing or blocking traffic based on the context of the communication.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): Advanced firewalls that incorporate deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and application-level security features.
4. Network Management and Security Best Practices
- Network Monitoring: Implement network monitoring tools to collect performance data, identify anomalies, and detect potential security threats.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy and maintain an IDS/IPS to detect and prevent malicious activity.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement and maintain ACLs to restrict network access and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all network devices and software updated with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and implement an incident response plan to effectively handle security breaches and minimize their impact.
5. Use Cases
- Protecting a Corporate Network: Implementing a layered security approach with firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls to protect sensitive data and business operations.
- Securing a Data Center: Implementing robust security measures to protect critical infrastructure and data within a data center environment.
- Securing Cloud Environments: Implementing security controls in cloud environments, including virtual firewalls, network segmentation, and access controls.
References:
- "Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach" by James F. Kurose and Keith W. Ross
- "Data Communications and Networking" by Behrouz A. Forouzan
- "Network Security: Private Communication in a Public World" by William Stallings
- Gartner: https://www.cisco.com/ (For information on Cisco networking and security solutions)
- Juniper Networks: (For information on Juniper networking and security solutions)
Disclaimer: This white paper provides a general overview of network management, security, and firewall solutions. The specific requirements and implementations will vary depending on the individual organization's needs and environment.
This information is for general guidance and may be subject to change. Always refer to the latest documentation and best practices for the most up-to-date information on network security and management.