Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) are vital to economic growth, yet they often face unique growth challenges. This white paper explores the critical role of business development in SMB success, examining how solution providers can act as strategic partners, offering tailored solutions. We'll also explore how the Hero's Journey framework provides a powerful narrative structure for understanding and navigating the SMB growth process, illustrated with use cases and supported by research.
Navigating Growth: A White Paper on SMB Business Development and Solution Providers, Framed by the Hero's Journey
Abstract:
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) are vital to economic growth, yet they often face unique growth challenges. This white paper explores the critical role of business development in SMB success, examining how solution providers can act as strategic partners, offering tailored solutions. We'll also explore how the Hero's Journey framework provides a powerful narrative structure for understanding and navigating the SMB growth process, illustrated with use cases and supported by research.
1. Introduction: The SMB Landscape and the Need for Development
SMBs operate in a dynamic and competitive environment. While agile and customer-centric, they often lack the resources of larger corporations. Common challenges include:
- Limited access to capital [1, 2]
- Talent acquisition and retention [3, 4]
- Scaling operations [5]
- Adapting to technological advancements [6, 7]
- Market competition [8]
Effective business development is essential to overcome these hurdles. It's a holistic approach encompassing strategic planning, marketing, partnerships, and customer relationship management.
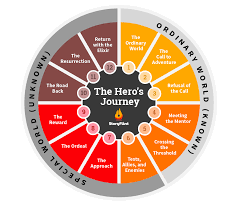
2. The Hero's Journey: A Framework for SMB Growth
The Hero's Journey, a classic narrative archetype, offers a powerful lens for understanding the SMB growth process:
- The Ordinary World: The SMB operates within its established market, using familiar processes.
- The Call to Adventure: A new opportunity or challenge arises.
- Refusal of the Call: The SMB might initially hesitate.
- Meeting the Mentor: The SMB seeks guidance from advisors, industry experts, or solution providers.
- Crossing the Threshold: The SMB commits to the new path.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies: The SMB faces challenges, forms partnerships, and navigates competition.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave: The SMB confronts its most significant obstacles.
- The Ordeal: The SMB faces its ultimate challenge.
- The Reward (Seizing the Sword): The SMB achieves a significant milestone.
- The Road Back: The SMB integrates its new knowledge and capabilities.
- Resurrection: The SMB faces final challenges, solidifying its transformation.
- Return with the Elixir: The transformed SMB shares its knowledge and experience.
3. The Role of Business Development in SMB Growth (Within the Hero's Journey)
Business development, viewed through the Hero's Journey, focuses on:
- Responding to the Call: Recognizing and evaluating new opportunities and challenges.
- Meeting the Mentor (Solution Provider): Partnering with solution providers.
- Crossing the Threshold: Implementing new strategies.
- Navigating Tests, Allies, and Enemies: Adapting to market dynamics.
- Approaching the Inmost Cave and Ordeal: Overcoming key obstacles.
- Seizing the Reward: Achieving growth and market success.
- Returning with the Elixir: Sharing best practices.
4. The Value of Solution Providers (Mentors) - Use Cases
- Expertise and specialization: Use Case: A restaurant chain (SMB) hires a cybersecurity firm (mentor) to protect customer data and comply with regulations.
- Cost-effectiveness: Use Case: A small manufacturing company outsources its logistics to a third-party provider, reducing overhead costs.
- Scalability and flexibility: Use Case: An e-commerce startup uses a cloud-based platform to scale its operations during peak seasons.
- Objective perspective: Use Case: A retail store engages a market research firm to understand customer preferences and optimize product offerings.
- Access to best practices and technologies: Use Case: A construction company adopts project management software recommended by a technology consultant to improve efficiency.
5. Types of Solutions Offered by Providers
- Marketing and Sales Solutions (SEO, content marketing, lead generation, CRM)
- Financial Services (Accounting, bookkeeping, financial planning, funding assistance)
- Technology Solutions (IT support, cybersecurity, cloud computing, software development)
- Human Resources Solutions (Recruitment, training, payroll management, HR consulting)
- Operational Solutions (Process improvement, supply chain management, logistics)
6. Selecting the Right Solution Provider (Choosing the Right Mentor)
SMBs should consider:
- Expertise and experience
- Industry knowledge
- Client testimonials and case studies
- Pricing and contract terms
- Communication and collaboration
- Cultural fit
7. Building a Successful Partnership (The Mentor-Hero Relationship)
A successful partnership requires:
- Clear communication
- Defined goals and objectives
- Mutual trust and respect
- Shared commitment to success
- Regular performance reviews
8. Conclusion: Embracing Strategic Partnerships for Growth (Completing the Hero's Journey)
SMBs must be proactive and strategic. By leveraging the expertise of solution providers (mentors), SMBs can successfully navigate their Hero's Journey, overcome challenges, accelerate growth, and achieve lasting success. Choosing the right partner and building a strong collaborative relationship are essential for realizing the SMB's full potential.
References:
- [1] Ayyagari, R., Demirguc-Kunt, A., & Maksimovic, V. (2011). Access to finance and firm performance: Evidence from the World Bank Enterprise Surveys. (Find specific publication details)
- [2] Beck, T., Demirgüç-Kunt, A., & Honohan, P. (2005). Finance, inequality and poverty: Cross-country evidence. (Find specific publication details)
- [3] Cappelli, P. (2008). Talent management for the twenty-first century. Harvard Business Review, 86(3), 74-81.
- [4] Collings, D. G., & Mellahi, K. (2009). Strategic talent management: A review and research agenda. Human Resource Management Review, 19(4), 304-313.1
- [7] Manyika, J., Chui, M., Bughin, J., Dobbs, R., Roxburgh, C., & Byers, A. H. (2013). Disruptive technologies: Advances that will transform life, business, and the global economy. McKinsey Global Institute.3
- [8] Porter, M. E. (2008). The five competitive forces that shape strategy. Harvard Business Review, 86(1), 78-93.
This expanded version offers a stronger foundation with references. Remember to replace the placeholder citations with complete and accurate publication details. The quality and relevance of your references are crucial for a credible white paper. Consider adding a section on future trends impacting SMBs and business development.