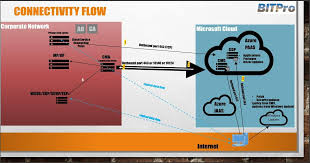
Understanding the Scope
Before we delve into the specifics, it's crucial to define the scope of your white paper. Here are some key considerations:
- Target Audience: Who are you writing for? IT professionals, security experts, or a broader audience?
- Level of Technical Detail: How deep do you want to go into technical intricacies?
- Specific Focus: Are you focusing on a particular type of content management gateway (CMG), a specific security concern, or a general overview?
Crafting a Comprehensive White Paper: Content Management Gateway for Security
Understanding the Scope
Before we delve into the specifics, it's crucial to define the scope of your white paper. Here are some key considerations:
- Target Audience: Who are you writing for? IT professionals, security experts, or a broader audience?
- Level of Technical Detail: How deep do you want to go into technical intricacies?
- Specific Focus: Are you focusing on a particular type of content management gateway (CMG), a specific security concern, or a general overview?
Key Sections of Your White Paper
- Introduction
- Define a CMG: A Content Management Gateway (CMG) is a software or hardware-based system that acts as a central hub for managing and controlling access to digital content within an organization. It provides a secure and efficient way to store, retrieve, and distribute content, while also enforcing security policies and protecting sensitive information.
- Highlight the security implications of CMGs: CMGs handle a vast amount of sensitive data, making them a prime target for cyberattacks. Security breaches can lead to data loss, financial damage, and reputational harm.
- Briefly outline the paper's objectives and structure: This section should provide a roadmap for the reader, outlining the key topics that will be covered in the paper.
- Security Challenges in Content Management Gateways
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality:
- Discuss the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access: Data breaches can result in the exposure of sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property. Unauthorized access can compromise the confidentiality and integrity of data.
- Explore encryption techniques and access controls to protect sensitive data: Encryption techniques, such as AES and RSA, can be used to encrypt data at rest and in transit. Access controls can be implemented to limit access to authorized users and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity:
- Address the importance of data integrity and the potential for tampering: Data integrity ensures that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. Tampering with data can lead to incorrect decisions and legal issues.
- Discuss hashing algorithms and digital signatures to ensure data authenticity: Hashing algorithms can be used to verify the integrity of data by creating a unique hash value. Digital signatures can be used to authenticate the source of data and ensure that it has not been tampered with.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks:
- Explain how DoS attacks can disrupt CMG operations: DoS attacks can overload a CMG's resources, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Discuss mitigation techniques like rate limiting and intrusion detection systems: Rate limiting can be used to limit the number of requests that a CMG can handle. Intrusion detection systems can be used to identify and block malicious traffic.
- Malware and Viruses:
- Highlight the risks of malicious code entering the system through CMGs: Malware and viruses can infect CMGs and spread to other systems, causing damage and disruption.
- Discuss antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems: Antivirus software can be used to detect and remove malware. Firewalls can be used to protect the CMG from external threats. Intrusion prevention systems can be used to block malicious attacks.
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality:
- Security Best Practices for CMGs
- Strong Authentication and Authorization:
- Implement robust authentication mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification,1 such as a password and a2 security token.
- Enforce granular access controls to limit user privileges: Granular access controls can be used to limit user access to specific resources based on their role and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
- Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities: Regular security assessments can help identify and address security weaknesses.
- Simulate attacks to assess the system's resilience: Penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Network Security:
- Implement firewalls to protect the CMG from external threats: Firewalls can be used to filter traffic and block malicious attacks.
- Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic: Intrusion detection systems can be used to identify and alert administrators to suspicious activity. Intrusion prevention systems can be used to block malicious traffic.
- Secure Configuration Management:
- Maintain secure configurations for all CMG components: Secure configurations can help prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Regularly patch and update software to address vulnerabilities: Software updates can address security vulnerabilities and improve the overall security of the CMG.
- Data Backup and Recovery:
- Implement regular backups to mitigate data loss risks: Regular backups can help protect data from accidental loss or deletion.
- Test recovery procedures to ensure their effectiveness: Recovery procedures should be tested regularly to ensure that they work as expected.
- Strong Authentication and Authorization:
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- Showcase successful security implementations in CMGs: This section can highlight real-world examples of organizations that have implemented effective security measures for their CMGs.
- Highlight lessons learned from security breaches and data leaks: This section can discuss the lessons learned from high-profile security breaches and data leaks, and how these lessons can be applied to improve CMG security.
- Conclusion
- Summarize the key security challenges and best practices: This section should provide a concise summary of the key security challenges and best practices discussed in the paper.
- Emphasize the importance of ongoing security monitoring and improvement: Security is an ongoing process, and organizations should continuously monitor their CMGs for security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Provide recommendations for future research and development: This section can suggest areas for future research and development, such as the development of new security technologies and best practices.
References
- Books:
- "Security Engineering" by Ross Anderson
- "The Art of Software Security Testing" by Gary McGraw
- Research Papers:
- Search academic databases like Google Scholar for papers on CMG security, network security, and data privacy.
- Websites:
- Security Standards Organizations: NIST, OWASP, ISO/IEC
- Cloud Service Providers: AWS, Azure, GCP (for cloud-based CMGs)
- Security Blogs and Forums: Dark Reading, SecurityFocus, Reddit's r/cybersecurity
Additional Tips- we are impproving this paper in the following areas
- Clear and Concise Writing: Use clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon where possible.
- Visual Aids: Use diagrams and flowcharts to illustrate complex concepts.
- Proofread Carefully: Ensure your white paper is free of errors and typos.
- Seek Feedback: Share your draft with colleagues and experts for feedback.
Would you like to delve deeper into a specific section or explore a particular aspect of CMG security? Contact keencomputer.com for details.